What is The Most Energy Efficient Heating and Cooling System?
Do you want to keep your home comfortable all year round without breaking the bank? If so, then choosing an energy efficient heating and cooling system is a must. With rising energy costs and increasing concern for the environment, it’s essential to find a system that not only reduces your utility bills but also helps reduce your carbon footprint. In this blog post, we’ll explore different types of heating and cooling systems, compare their energy efficiency ratings, and reveal which ones come out on top as the most efficient options available today!
Importance of Energy Efficiency in Heating and Cooling Systems
Energy efficiency has become a buzzword in the world of heating and cooling systems. It refers to the ability of these systems to consume less energy while providing the same level of comfort. The importance of energy efficiency cannot be overstated, especially when considering its impact on the environment, our homes, and our wallets.
Firstly, we all know that excessive use of electricity increases carbon emissions into the atmosphere. These emissions contribute significantly to global warming and climate change. Energy-efficient heating and cooling systems reduce carbon footprints by minimizing their power consumption.
Secondly, many homeowners face high utility bills due to inefficient HVAC (heating ventilation air conditioning) systems. An energy-efficient system can help them save money on their monthly bills through reduced power usage without sacrificing comfort levels.
Furthermore, an efficient HVAC system is more reliable as it experiences fewer breakdowns leading to lower maintenance costs over time.
In summary, energy efficiency is essential for reducing environmental impacts while saving money for homeowners by reducing utility bills and ensuring that HVAC systems operate smoothly with minimal downtime or repairs required.
Overview of Different Types of Heating and Cooling Systems
When it comes to heating and cooling systems, there are several types available on the market. Each type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages that homeowners need to consider before choosing a system for their home.
Furnaces
Furnaces are a type of heating system that use natural gas, propane, or electricity to produce heat in the home. They work by heating air and distributing it through ducts throughout the house. Furnaces have been a popular choice for decades due to their reliability and affordability.
When choosing a furnace, it’s important to consider its energy efficiency rating, also known as AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency). A higher AFUE rating means that the furnace will use less fuel and be more efficient at converting fuel into heat.
One downside of furnaces is that they can create dry air in the home, which can lead to respiratory problems if not addressed. However, this can be mitigated with the use of humidifiers or by installing a whole-house humidifier.
Another consideration when choosing a furnace is whether you want one with single-stage or two-stage operation. Single-stage furnaces only have one output level while two-stage furnaces have high and low output levels depending on how much heat is needed.
While there are other more energy-efficient options available such as geothermal systems or ductless mini-split systems, furnaces remain an affordable and reliable option for many homeowners.
Central Air Conditioners
Central air conditioners are a popular choice for cooling homes and buildings. They use a centralized duct system to deliver cool air throughout the space, making them ideal for larger or multi-level properties.
These systems work by drawing warm air from inside the home through return vents, which then passes over evaporator coils filled with refrigerant. The refrigerant absorbs heat and moisture before being sent outside to be cooled by the condenser unit. The now-cooled air is then pushed back into the home through supply vents.
When selecting a central AC unit, it’s important to consider its SEER rating (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio). A higher SEER rating indicates better energy efficiency and can translate into lower utility bills.
Regular maintenance is also crucial in keeping your central AC operating efficiently. This includes changing filters regularly, cleaning both indoor and outdoor components, and scheduling professional tune-ups as needed.
Central AC units can provide efficient cooling for larger spaces when properly maintained and chosen with energy efficiency in mind.
Heat Pumps
Heat pumps are becoming a popular choice for homeowners looking to upgrade their heating and cooling systems with energy efficiency in mind. Unlike traditional furnaces or air conditioners, heat pumps can both heat and cool a home using less energy.
During the winter months, heat pumps extract heat from outside air and transfer it inside to warm up the home. In contrast, during the summer months, they work in reverse by moving hot air out of the house to cool it down.
One advantage of choosing a heat pump over other types of systems is its high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating. The higher the rating, the more efficient the system is at converting electricity into cooling power.
Another benefit of heat pumps is their HSPF (Heating Season Performance Factor) ratings, which measure their efficiency in heating mode specifically. This makes them an excellent option for areas with mild winters as they provide warmth without relying on fossil fuels like natural gas or propane.
If you live in an area with moderate temperatures year-round and want a system that can both cool and heat your home efficiently while being environmentally friendly, then a heat pump might be worth considering.
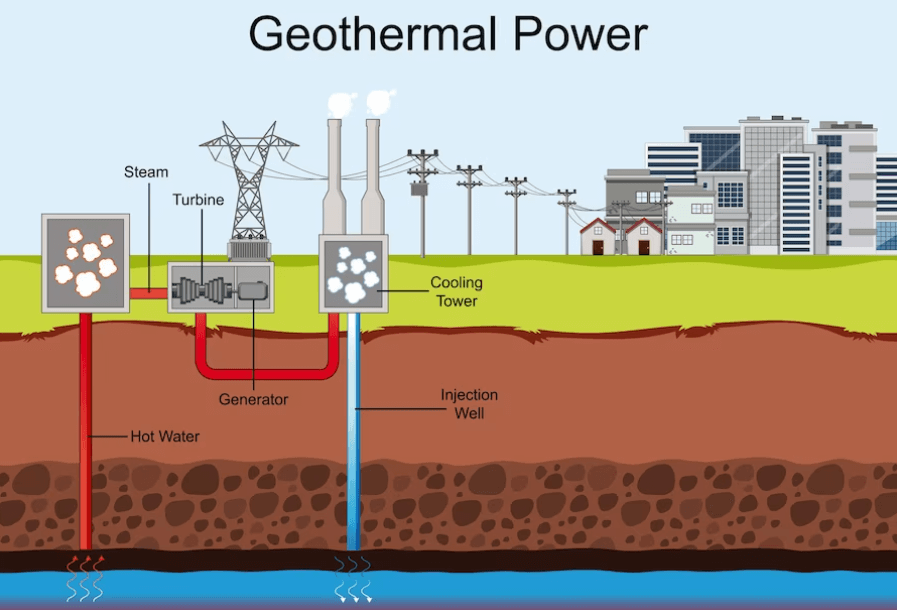
Geothermal Systems
Geothermal systems are one of the most energy-efficient heating and cooling options available. These systems use the constant temperature of the earth to regulate indoor temperatures, making them a reliable and consistent choice for homeowners.
The system works by exchanging heat between the ground and a fluid-filled loop that runs through pipes installed underground. The heat is then carried into a compressor unit where it’s converted into warm or cool air for your home.
One major advantage of geothermal systems is their long lifespan – up to 25 years for inside components and up to 50 years for underground loops. They’re also extremely quiet and require little maintenance compared to traditional HVAC units.
While geothermal systems do have higher upfront costs, they can save homeowners money in monthly energy bills over time. Additionally, these types of systems are environmentally friendly as they don’t rely on fossil fuels or emit harmful greenhouse gases.
If you’re looking for an efficient and eco-friendly heating/cooling option with long-term benefits, consider getting a geothermal system installed in your home.
Ductless Mini-Split Systems
Ductless mini-split systems are a type of heating and cooling system that don’t require ductwork to function. They consist of an outdoor unit connected to one or more indoor units, which can be installed in different rooms or zones throughout the house.
One of the advantages of ductless mini-splits is their energy efficiency. Unlike central air conditioners or furnaces, these systems allow for zone-specific temperature control, eliminating the need to heat or cool unoccupied areas.
Another benefit is their ease of installation. Ductless mini-splits can be up and running in as little as a day, with no major construction required.
In addition, these systems offer quiet operation and improved air quality compared to traditional HVAC setups. The absence of ductwork means there’s less opportunity for dust and allergens to circulate throughout the home.
When it comes to choosing a ductless mini-split system, it’s important to consider factors such as room size and layout, as well as the climate in your area. Consulting with a professional installer can help ensure you choose the right system for your needs.
Comparing the Energy Efficiency of Different Systems
When it comes to choosing an energy efficient heating and cooling system, it’s important to compare the different options available. One way to do this is by examining the SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings for air conditioners and HSPF (Heating Season Performance Factor) ratings for heaters.
SEER measures the cooling output of an air conditioner over a season, divided by its energy consumption. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the unit is at cooling your home. Meanwhile, HSPF measures how efficiently a heat pump can provide warmth during colder months.
Another factor to consider when comparing systems is their age and maintenance needs. Older units tend to be less efficient than newer models due to advancements in technology. Regular maintenance such as changing filters or cleaning coils can also improve efficiency.
It’s important not only to consider individual components but also how they work together within a system. A well-designed HVAC system that matches your home’s size and layout will run more efficiently than one that is improperly sized or poorly installed.
By carefully considering factors like SEER/HSPF ratings, age/maintenance needs, and proper sizing/installation, you can make an informed decision about which energy-efficient heating and cooling system best suits your specific needs.
The Most Energy Efficient Heating and Cooling Systems
When it comes to selecting the most energy-efficient heating and cooling systems, there are a few options that stand out. Geothermal heat pumps and ductless mini-split systems are both highly efficient choices.
Geothermal heat pumps utilize the stable temperature of the earth to provide heating and cooling for your home. By extracting heat from the ground or water source, these systems can achieve a coefficient of performance (COP) between 3 and 6. This means they can produce up to six times as much energy as they consume.
Ductless mini-split systems use an outdoor compressor unit connected to indoor air handlers via refrigerant lines. They allow you to control temperatures in different zones throughout your home independently, reducing wasted energy by only conditioning rooms that need it.
Both geothermal heat pumps and ductless mini-splits have high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) ratings for cooling efficiency and Heating Season Performance Factor (HSPF) ratings for heating efficiency.
Of course, choosing an energy-efficient system also depends on factors such as climate and home size/layout. Consulting with an HVAC professional is always recommended when making this important decision.
Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps are a highly efficient, eco-friendly heating and cooling system that utilizes the earth’s natural energy to regulate the temperature inside your home. Unlike traditional HVAC systems, which rely on fossil fuels, geothermal systems use the consistent temperature of underground soil to provide year-round comfort.
These systems work by circulating water or refrigerant through pipes buried in the ground. The liquid absorbs heat from the earth during winter months and transfers it into your home for warmth. In summer months, this process is reversed as heat is removed from your home and transferred back into the ground.
The efficiency of a geothermal system stems from its ability to harness renewable energy sources rather than relying on non-renewable fuels. This means lower carbon emissions and reduced reliance on foreign oil.
While initial installation costs can be higher than other types of heating and cooling systems, homeowners can recoup these expenses over time through significant savings on utility bills due to increased efficiency ratings. Geothermal systems also have longer lifespans compared to traditional HVAC units making them a long-term investment for your home’s sustainability.
Ductless Mini-Split Systems
Ductless mini-split systems are a great option for homeowners who want an energy-efficient and flexible heating and cooling solution. Unlike traditional HVAC systems, ductless mini-splits don’t require bulky ductwork to distribute air throughout your home. Instead, they use small refrigerant lines that run from an outdoor unit to one or more indoor units.
One of the benefits of ductless mini-splits is their flexibility. They can be installed in almost any room or area of your home, making them ideal for homes without existing ductwork or where adding new ducts would be difficult or expensive.
Another advantage of these systems is their high energy efficiency ratings. Ductless mini-split systems typically have SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings between 18-30 and HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) ratings between 8-12, which means they’re highly efficient at both heating and cooling your home.
Because each indoor unit operates independently, you can set different temperatures in different rooms based on individual preferences. This allows for greater control over your home’s comfort levels while also reducing energy waste by not heating or cooling unused rooms.
If you’re looking for a cost-effective and customizable HVAC solution that doesn’t require invasive installation procedures like traditional central air conditioning units do – then a ductless mini-split system may be right for you!
Considerations When Choosing an Energy Efficient System
When choosing an energy-efficient heating and cooling system, there are a few important factors to consider. First, you should take into account the climate of your region. Some systems work better in cooler climates while others are more suited for warmer areas.
Another consideration is the size and layout of your home. A larger home may require a more powerful system to adequately heat or cool all areas, while smaller homes may be able to use smaller systems that consume less energy.
It’s also important to look at SEER ratings for air conditioners and HSPF ratings for heat pumps. These ratings indicate how efficiently the system operates, with higher numbers indicating greater efficiency.
You should consider any additional features or technologies offered by different systems such as zone control or programmable thermostats. These can help increase energy efficiency by allowing you to only heat or cool specific areas at certain times.
Taking these factors into account when choosing an energy efficient heating and cooling system can help ensure that you select the best option for your home’s needs while also saving money on energy costs in the long run.
Conclusion
Energy efficiency is crucial when it comes to heating and cooling systems. Not only does this help save money on utility bills, but it also reduces the carbon footprint of a household. When choosing an energy efficient system, homeowners should consider factors such as climate and home size/layout.
Among the different types of heating and cooling systems available in the market today, geothermal heat pumps and ductless mini-split systems are considered to be the most energy efficient options. These two options have higher SEER ratings for air conditioning and HSPF ratings for heating than other traditional HVAC units.
While there may be upfront costs associated with installing these more advanced systems, they can provide long-term savings through lower monthly energy bills. Ultimately, choosing an energy-efficient system not only saves you money but also helps protect our planet by reducing your carbon footprint.
Recent Queries: